In our example we create a mapping from a CSV text file, source of the data transfer, to the target JDBC data source, see Example CSV source and Example JDBC target for details. The last step in defining the Data transfer action (DTA) is to create a mapping between these data sources, and this will now be discussed.
The JDBC data source provides generic access to all commonly available databases and may be either a source or target of a data transfer action, see JDBC data source overview. During a mapping source tables and columns are transformed into target tables and columns and you may synchronize new data with existing data in a target data source, using the Select / Update procedures. In addition in JDBC data sources we must deal with generated unique keys and foreign keys when creating records in the target database when the target data source does not automatically generate keys on insertion. We have these options:
getKeyFromQuery- returns a value from an SQL query.
getKeyFromKeyTable
- returns a value from a predefined key generation table. It requires
the user to specify what the table name is and what the column names are.
getAutoNumberKey
- specifies that the key will be generated by the database on insertion.
getMaxKey
- specifies that the key will be generated by asking for the maximum key
already in the table and adding one.
These functions use data in the target database to generate a unique key for each new record of the specified entity that is inserted into the database.
In our present example, table OrderHeader contains the header details for each order, OrderLine contains order lines, and Product_Lookup is assumed to be a lookup table to find product descriptions from a product code.
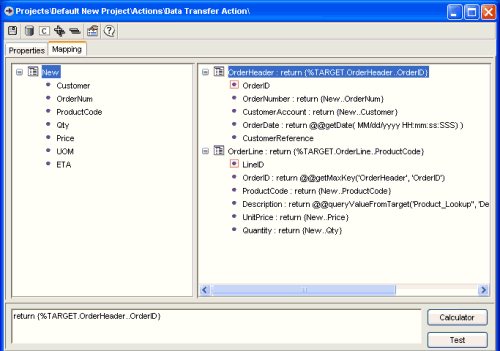
We will create mappings from source to target data sources using the Mapping tab, in some cases simply dragging source fields to target fields, and in other cases using the Calculator to introduce additional calculations, lookups etc. Here is an illustration of the Mapping panel that sets the target calculations:

On the left is the CSV file data entity with fields expanded. On the right is the JDBC target of the transfer, with the calculations showing how the database is to be created.
In some cases a field in the source has been simply dragged to the field in the target. For example field OrderNum in the New entity in the Source data source on the left, has simply been dragged to field OrderNumber of entity OrderHeader on the right, creating a simple field mapping. Similarly source fields Customer, ProductCode, Qty, Price, UOM have been dragged to the column headings CustomerAccount, ProductCode, Quantity, UnitPrice on the right, creating more simple field mappings.
In other cases however the target column has been selected on the Mapping screen, then the Calculator button pressed to give access to the source and target fields, functions, operators and other resources from the in-built Calculator, use these links to find out more. In fact the illustrated mapping uses a number of different techniques to populate data in the destination database:
Grouping: Dragging a target field to a target entity performs a Grouping Calculation, indicating to the system what field is used to determine new target entities, see Grouping Calculations for more. in this example column OrderID is unique to the OrderHeader table, so this field was dragged to this entity to automatically create the first grouping calculation. Similarly the ProductCode entity is unique to each OrderLine, so dragging this field to this target entity created the second target Grouping.
Key generator: The getMaxKey(..) key generator is used to get the last value of a generated key field to copy to another field (the OrderID field of the OrderLine entity). The function @@getMaxKey('OrderHeader','OrderID') instructs the system to get the highest value of the key field OrderID in the OrderHeader table and use this to populate the OrderID field in the OrderLine table. See Key generator functions for further discussion.
Date generator: Because our source data does not include an order date, the destination JDBC data source generates its own date using the getDate function. The format of the generated date is controlled by the format string applied to the getDate function - getDate('MM/dd/yyyyHH:mm:ss:SSS') will get the current date in a US date format complete with time - 7/18/2002 14:22:13:231 for example. See Date utilities for further details on the date format string.
Lookup table: In our destination tables we want to populate the product description field with a full description of the product, but our source data only has a product code. We use a lookup table in the destination data source to hold each possible product code and its description. The table Product_Lookup has just two columns - Code and Descript and the function queryValueFromTarget('Product_Lookup', 'Descript', 'Code', {New..ProductCode}) will return the description for a product based on a match of the source ProductCode field against the Code column in the lookup table. See Key generator functions for further details on these functions.
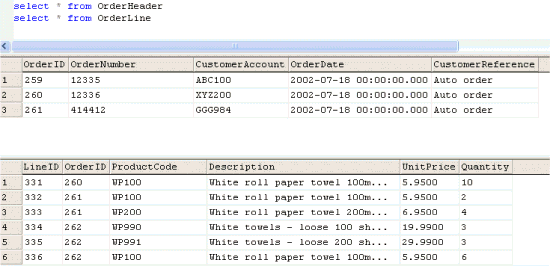
After executing the data transfer above, the resulting database data would be generated from the source CSV file above, as shown by the following SQL queries:
Related topics include Example CSV source, Example JDBC target, Data transfers overview, Mapping, Key generator functions, Grouping, Select / Update criteria, Calculations overview